Explaining the POPIT Model
by Etienne Pretorius

POPIT (People, Objectives, Processes, Information, and Technology) is a model that provides a holistic view of a business system by considering five key elements.
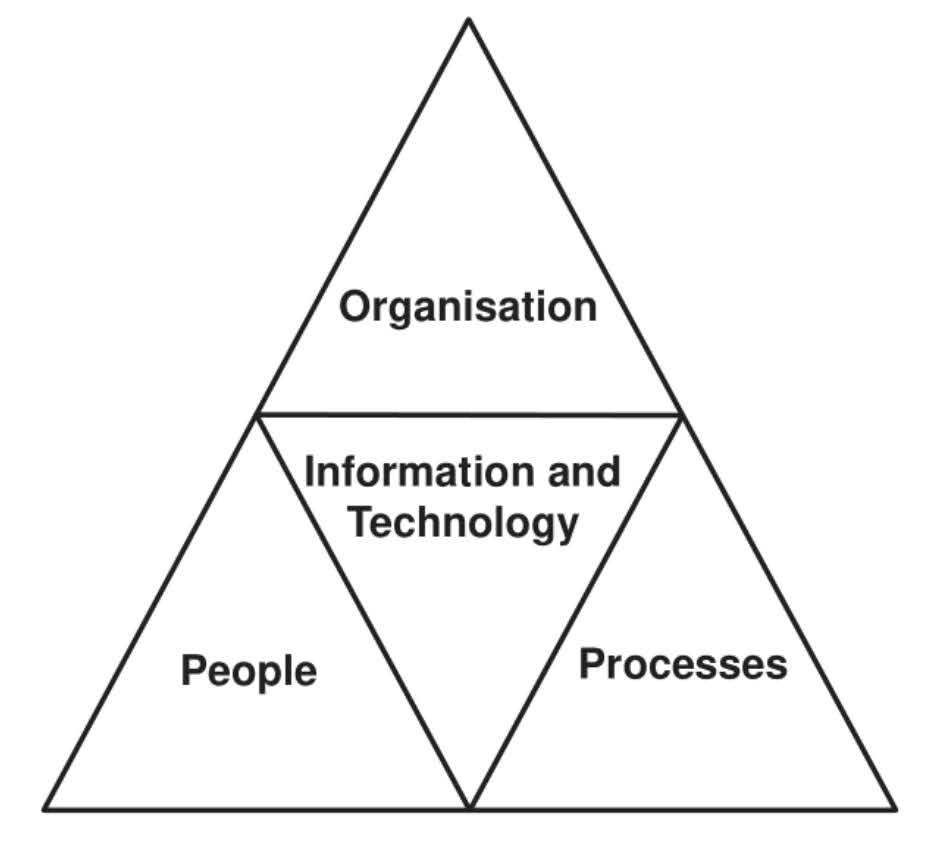
People: This element focuses on the people involved in the business system, including employees, customers, and stakeholders. Do they have the required skills and support to carry out the work? How motivated are they? Do they understand the business objectives that they need to support?
Organisation: This element defines the goals and objectives of the business system, including its mission, vision, and objectives. Are roles and responsibilities well defined? Is there a supportive management style? Is there collaborative cross-functional working? Does the culture enable productive work?
Processes: This element focuses on the processes involved in the business system, including workflows, business rules, and procedures. Are they efficient, well defined and communicated? Do they meet the performance measures expected by customers? Is there good technology support or are there several ‘workarounds’ in existence? Do the processes require information or documents to be passed around the organisation unnecessarily? Is there the potential for delays or the introduction of errors?
Information: This element deals with the data and information used by the business system, including data management and analysis. Do the staff have the information to conduct their work effectively? How is this information accessed? Are managers able to make decisions based on accurate and timely information?
Technology: This element focuses on the technology used by the business system, including hardware, software, and network systems. Do the software products support the business as required? Are they usable and accessible? Do they enable the organization to meet staff and customer needs?
The POPIT model is useful in a variety of scenarios, including system design and development, process improvement, and IT planning. It can be used to identify areas for improvement, optimize processes, and ensure that technology is aligned with business objectives.
Advantages of the POPIT model include its comprehensive view of the business system, its ability to identify areas for improvement, and its use in aligning technology with business objectives.
Drawbacks of the POPIT model include its complexity, the time and resources required to implement it, and the need for continuous monitoring and updating.
Here is a more comprehensive list of those advantages and drawbacks:
Advantages:
- Easy to use and implement: The POPIT model is simple and user-friendly, making it easy to implement in various organizational structures.
- Cost-effective: POPIT is an affordable model, making it accessible to organizations of different sizes and budget levels.
- Customizable: The model can be adapted to fit different organizational needs and goals, making it flexible and adaptable.
- Improves communication: POPIT facilitates effective communication between employees and departments, improving overall efficiency and productivity.
- Increases accountability: The model helps to increase accountability among employees, as it makes it clear who is responsible for what.
- Enhances decision-making: POPIT provides a structure for making decisions, reducing the risk of misunderstandings and increasing the chances of successful outcomes.
- Enhances collaboration: The model encourages collaboration between different departments and employees, promoting teamwork and a sense of unity.
- Improves performance: POPIT helps organizations to improve performance by providing a clear framework for planning and execution.
- Facilitates goal-setting: The model makes it easier for organizations to set goals and track progress, providing a clear roadmap for success.
- Increases motivation: POPIT helps to increase motivation among employees, as it provides a clear sense of purpose and direction.
Drawbacks:
- Resistance to change: Some employees may resist the implementation of the POPIT model, as it represents a change from their traditional working practices.
- Lack of flexibility: The model may be rigid and inflexible, making it difficult to adapt to changing circumstances and conditions.
- Complexity: For larger organizations, the POPIT model may be too complex to implement effectively, as it requires a significant amount of time and resources.
- Lack of customization: The model may not be suitable for all organizations, as it may not be customizable enough to meet specific needs and requirements.
- Overreliance on technology: The model relies heavily on technology, which may cause problems if the technology fails or is unavailable.
- Poor implementation: The POPIT model may not be effective if it is not implemented correctly, as it requires a clear understanding of the organization’s goals and objectives.
- Resistance from management: Management may resist the implementation of the POPIT model, as it represents a change from their traditional decision-making processes.
- Risk of information overload: The model may result in information overload, as it requires a significant amount of data to be gathered and processed.
- Loss of creativity: The model may stifle creativity and innovation, as it provides a rigid structure for decision-making and problem-solving.
- Difficulty in measuring success: The model may be difficult to measure the success of, as it is not always easy to determine if it is delivering the desired results.
A consultant would use POPIT in situations where a business is looking to optimize its processes, align its technology with its objectives, or improve its overall performance. The consultant would use the model to identify areas for improvement, develop a plan to address those areas, and monitor the results.
ChatGPT Jan 9 Version.
