Managing Stakeholder’s and Stakeholder Analysis
by Etienne Pretorius

Analysing stakeholders in a project is an important task for any project manager, as the success of the project depends on how well the stakeholders are managed. Stakeholders can have a significant impact on the project, both positively and negatively. To assess the weight that should be attached to their issues, it is necessary to analyse their positions and interests in the project. The power/interest grid is a useful technique for this analysis.
The power/interest grid is a visual tool that helps to understand the relationship between the power and interest of stakeholders in a project. Power refers to the influence that a stakeholder has over the project, while interest refers to the stakeholder’s level of involvement in the project. The grid is divided into nine combinations of power and interest, ranging from high power/high interest to low power/low interest.
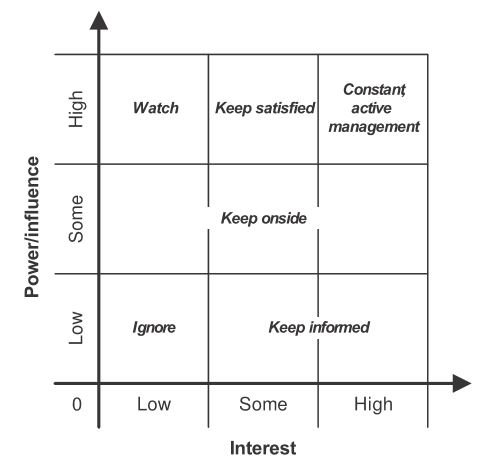
To use the power/interest grid, the stakeholders’ initial positions must be plotted. For example, consider a project to build a new office building. The stakeholders might include the project sponsor, project team, local residents, local council, and the construction company. The positions of each stakeholder can be plotted on the grid based on their level of power and interest in the project.
Once the initial positions of the stakeholders have been plotted, a plan can be drawn up for managing each of them. A one-page assessment can be made for each stakeholder, or a spreadsheet can be set up to see all stakeholders at a glance. The categories used for each stakeholder include champion, supporter, neutral, critic, opponent, and blocker.
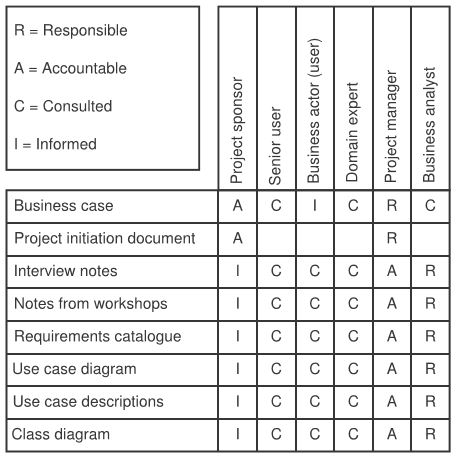
The responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed (RACI) chart is an excellent technique for clarifying an individual’s role and responsibilities in the project. This chart helps to define the role and responsibilities of business representatives in the project.
In some cases, it may be necessary to take action to increase a stakeholder’s active involvement in the project. This could involve designating them as the domain expert or project sponsor, or involving them in a particular committee. Alternatively, a more active approach may be necessary, such as meeting with stakeholders to engage their interest in the project.
In conclusion, managing stakeholders in a project is essential to its success. The power/interest grid is a useful technique for analysing the stakeholders, and the RACI chart is an effective method for clarifying roles and responsibilities. Positive management, such as frequent meetings and discussions, can help to keep stakeholders informed and involved in the project, and to detect changes in opinions or issues.
ChatGPT Jan 30 Version
